Technology of the Future in Moldova — Available Today!
HERE’S HOW TO SAVE YOUR SPINE AND LIVE WITHOUT BACK PAIN!
LIVING WITHOUT BACK PAIN IS NORMAL!
NON-SURGICAL TREATMENT OF HERNIATED DISCS AND MINIMALLY INVASIVE BIPORTAL ENDOSCOPY
HERE’S HOW TO SAVE YOUR SPINE AND AVOID BECOMING DISABLED!
How common is a condition like a herniated intervertebral disc, and how serious is it?
A person who has never experienced constant or occasional back pain is more the exception than the rule — 85-90% of the world’s population suffers from it. One of the most frequent causes of back pain is herniated discs. People often experience discomfort, and the pain can radiate to the buttocks and legs. They have to limit their movement and often take medications.
Doctor, first, let’s find out where hernias most often occur and why?
A herniated intervertebral disc most commonly occurs in the lumbosacral region of the spine, less frequently in the cervical and thoracic regions.
Most common causes:
- Static overload — overload caused by staying in one position for a long time. Both sitting and standing postures are equally harmful. This affects drivers, hairdressers, office workers.
- Dynamic overload — related to lifting heavy objects. This includes loaders, professional athletes.
- Injuries, fractures, vertebral bruises.
- Presence of osteochondrosis.
- Presence of scoliosis.
- Excess body weight.
How can a person suspect they have a herniated intervertebral disc?
Signs and symptoms of an intervertebral hernia:
Numbness in limbs, shooting pain, weakness; in severe and advanced cases — dysfunction of pelvic organs, muscle atrophy, foot drop.
In the cervical region: Severe headaches, often pulsating in nature, dizziness, weakness, feeling of oxygen deficiency, high blood pressure, numbness in the fingers, pain, and stiffness in the neck area.
In the thoracic region: Burning and pain in the chest, pseudocardialgia (many patients think it’s heart pain), pain, and sometimes loss of skin sensitivity between the shoulder blades.
Symptoms of hernia in the lumbosacral region: Numbness in the lower limbs, sharp, shooting pain in the lower back when bending or lifting weights, weakness in the legs (“uncontrollable legs”). In severe cases, problems with bowel movements and/or urination (incontinence or urinary retention).
For diagnosis of intervertebral hernia, first, a specialist examination is required by an orthopedist-vertebrologist, neurologist, or neurosurgeon. If necessary, the doctor orders MRI, CT scan, X-rays, or electromyography. No special preparation is required for these examinations.
What methods does modern medicine use to fight this disease?
Of course, everyone wants to get rid of pain without surgery. Fortunately, about 80 percent of herniated intervertebral discs respond well to conservative treatment. This includes prescribing nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, anti-edema medications, muscle relaxants, vascular-strengthening and vitamin supplements, and chondroprotectors. If no improvement is observed after six weeks of medication therapy, surgical intervention becomes inevitable. However, surgery does not go without consequences: scars often remain, which later provoke the same symptoms as the hernia, and there is a high rate of complications and unsuccessful treatment outcomes. In the literature, there is even a special term for this — “failed back surgery syndrome” or “flat back syndrome.” Despite the undeniable successes and advancements in spinal surgery, the incidence of failed back surgery syndrome remains very high. In Moldova, no one tracks this statistic, but in the United Kingdom — a country far ahead of Moldova in medical technology — more than 2,000 cases of failed back surgery syndrome are registered annually.
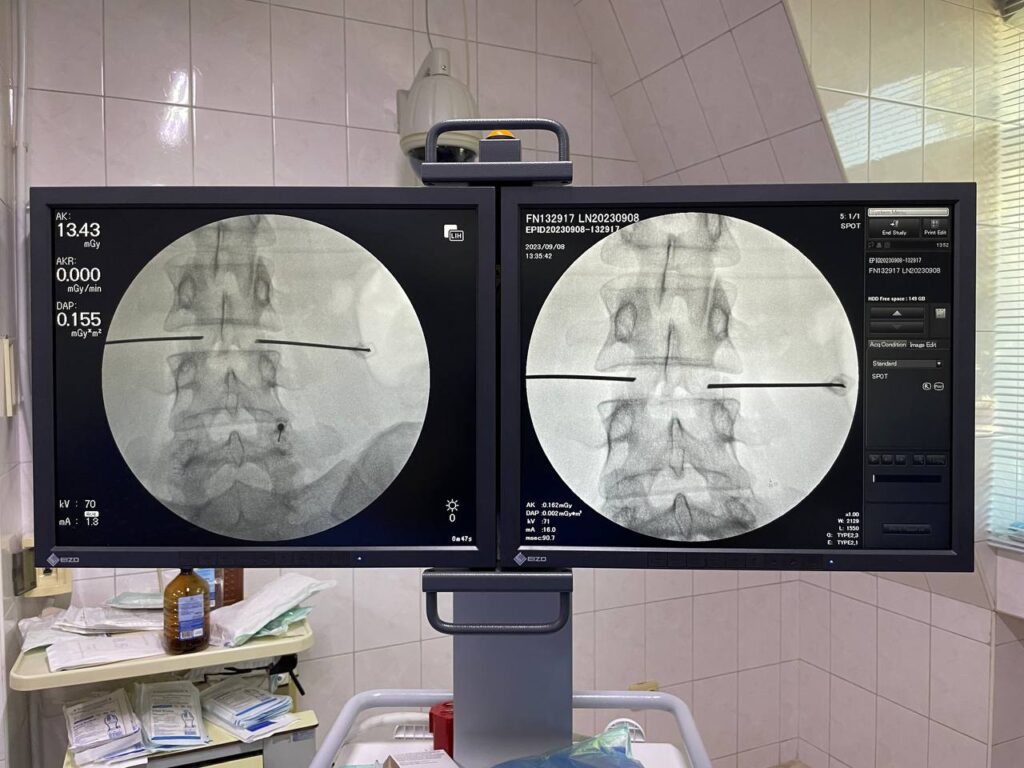
If the hernia is small, we offer patients a non-surgical treatment method — a puncture method, simply put, an injection into the disc. This is the Cold Plasma Nucleoplasty method, in which a very thin electrode is inserted into the herniated nucleus pulposus. At a temperature of 40–50°C, the structures of the intervertebral disc are “vaporized.” As a result, the hernia retracts and stops pressing on the nerve roots, and pain and other unpleasant symptoms disappear.
Cold Plasma Nucleoplasty serves as a bridge between conservative therapy — which at a certain stage of the disease ceases to be effective — and spinal surgery (discectomy), which in most cases is the final treatment option.
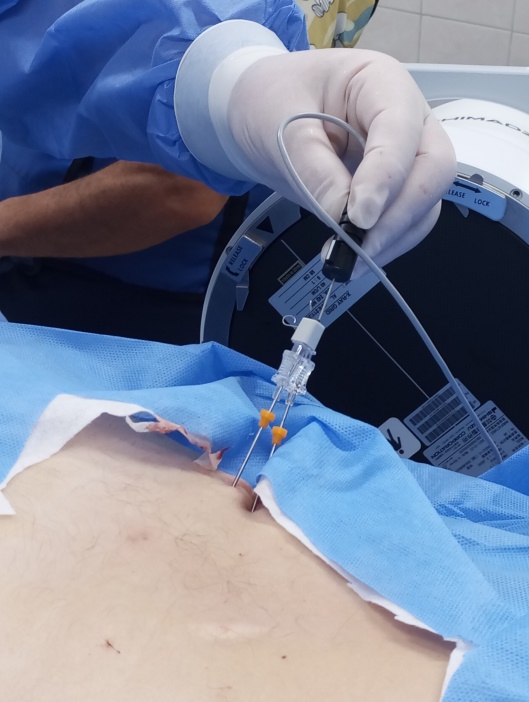
DISCOGEL THERAPY
Percutaneous injection of a special gel-like substance into the intervertebral disc where the hernia has formed. By drying out the hernia, it hardens and forms a “prosthesis” that replaces the damaged disc.
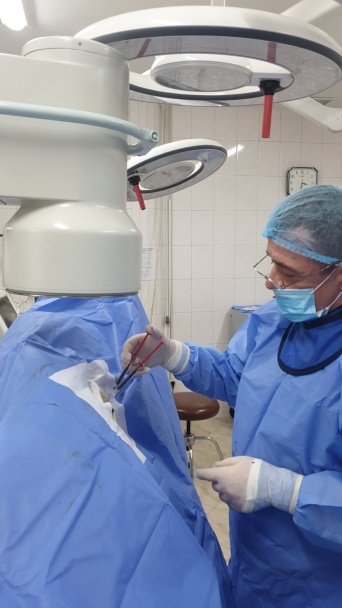
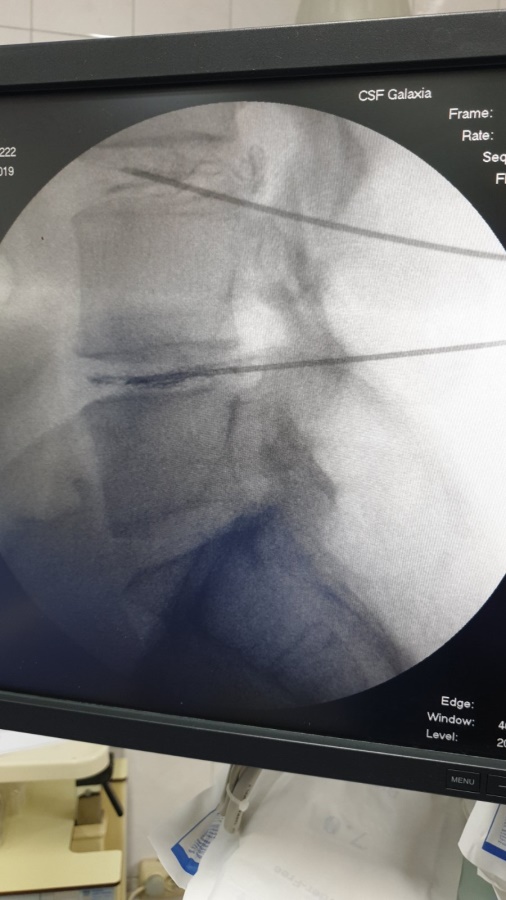
What should be done if the hernia is already large?
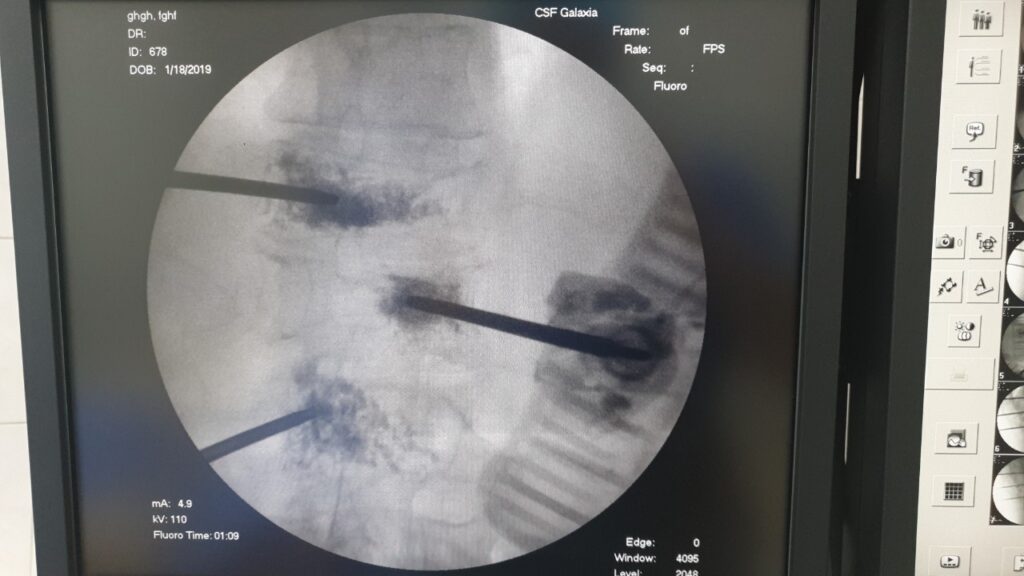
If the hernia is already large, we offer the endoscopic UBE method (unilateral biportal endoscopy).
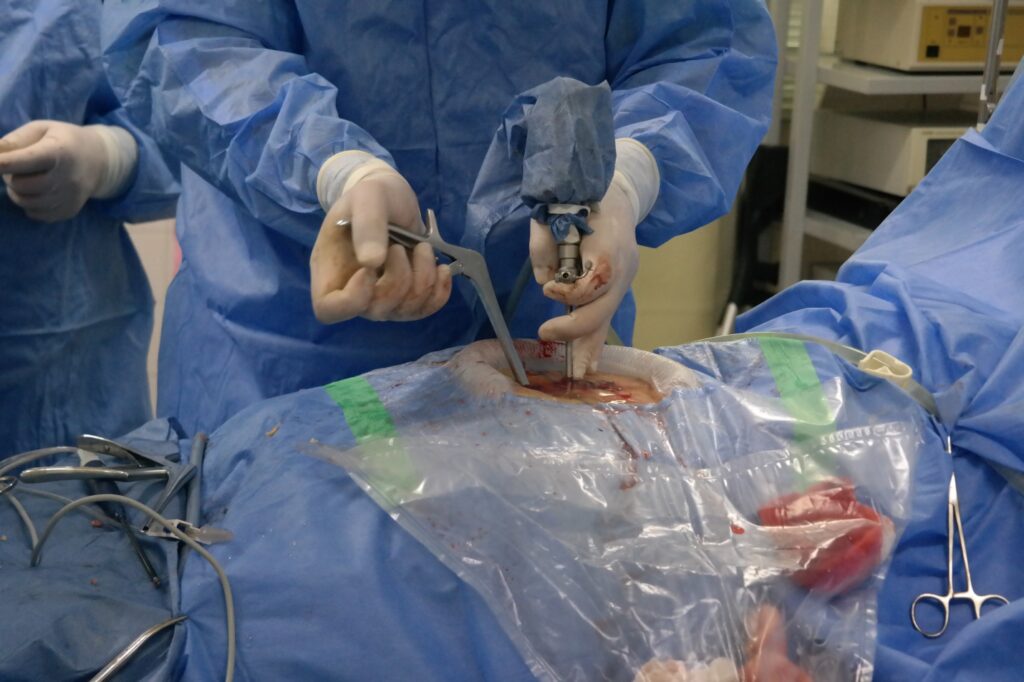
Can you tell me a little more about this method?
The UBE endoscopic method (unilateral biportal endoscopy) is a cutting-edge minimally invasive surgical procedure for removing a disc hernia that compresses nerve roots and spinal nerves, causing pain. This technique minimizes damage to soft tissues by targeting only the pathological area precisely.
The surgery typically takes about 1 hour and is performed using modern endoscopic equipment and micro-instruments, under either general or local anesthesia. Before the operation, the surgeon precisely locates the herniated intervertebral disc and makes two small incisions on the skin, each only 7-8 mm long. Through one incision, an endoscope is inserted, transmitting a magnified image to a monitor, while surgical instruments are introduced through the other incision to remove the hernia. This approach completely avoids damaging healthy tissues, and recovery after surgery is easy and quick. Within 2-3 hours after the endoscopic procedure, the patient can sit up, move independently around the ward, use the restroom, and take a shower. The hospital stay is typically just one day, making this neuroendoscopic treatment of intervertebral disc hernias a “day surgery” procedure.
This allows patients to avoid strict bed rest and prolonged disability. Pain in the spine usually disappears immediately after the intervention, but neurological symptoms such as weakness and numbness in the limbs may persist for some time. In some cases, paralysis may be irreversible if treatment is delayed. The outcome largely depends on timely consultation with a neurosurgeon. The earlier the patient receives necessary treatment, the better the surgical result will be.
Thus, the UBE endoscopic method (unilateral biportal endoscopy) offers:
- Effectiveness and Safety
Proven high treatment efficacy with no recurrences or side complications. - Minimal Trauma
The minimally invasive nature of the procedure helps avoid blood loss and muscle damage. - Fast Recovery
Short hospital stay and rehabilitation period (one day) enable a quick return to an active life. - Improved Quality of Life
No significant pain syndrome or scars, unlike with traditional surgeries.
It is worth noting that the “Galaxia” clinic is the first and only clinic in Moldova where hernia removal is performed using this UBE method.
At our clinic, you can receive a full range of treatments for back pain—from conservative medication therapy, manual therapy, and physiotherapy to non-surgical hernia removal, minimally invasive endoscopic spinal surgery, and, if necessary, major reconstructive operations.
— Vertebroplasty — an endoscopic procedure to strengthen the spine using “bone cement.” It is indicated for hemangiomas, compression fractures of the spine, and tumors.
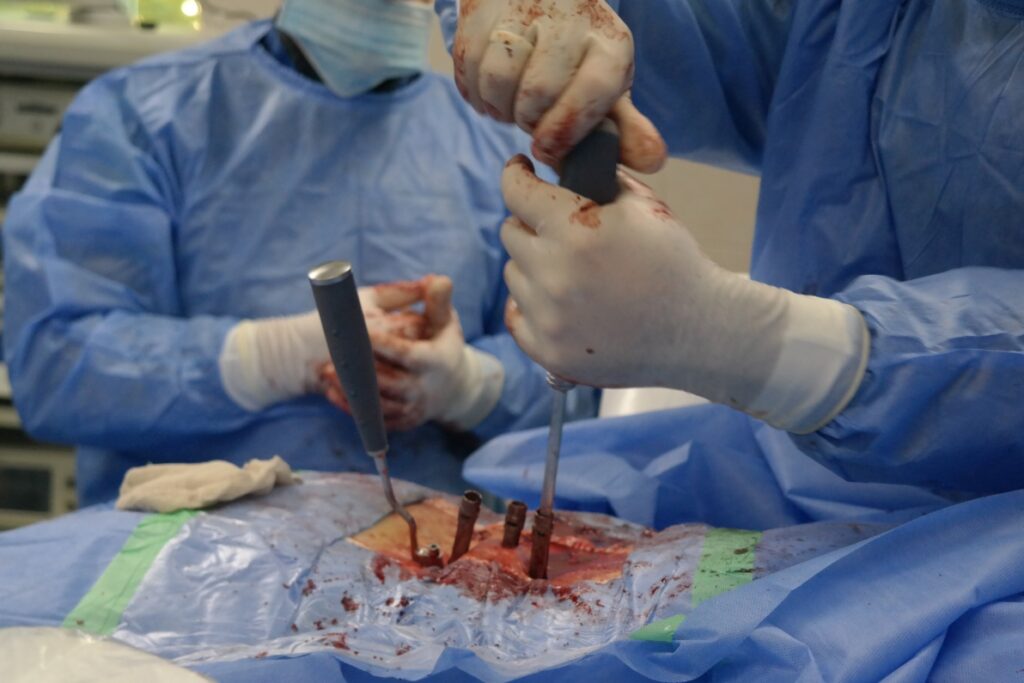
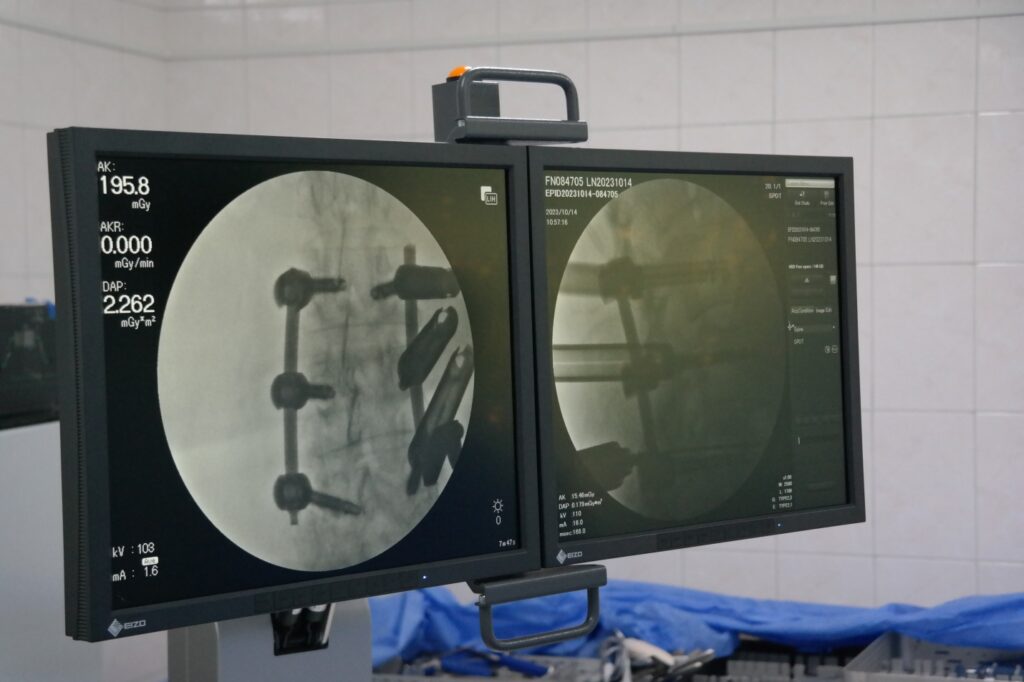
— Transpedicular spinal fixation — an endoscopic surgery in which the vertebrae are fixed and stabilized using special implants (transpedicular screws). It is indicated for unstable spinal fractures, recurrent disc herniation, osteochondrosis, scoliosis, spondylolisthesis, and spinal canal stenosis.
THERE ARE NO BETTER OR WORSE TREATMENT METHODS, THERE IS THE BEST TREATMENT METHOD FOR EACH INDIVIDUAL PATIENT.