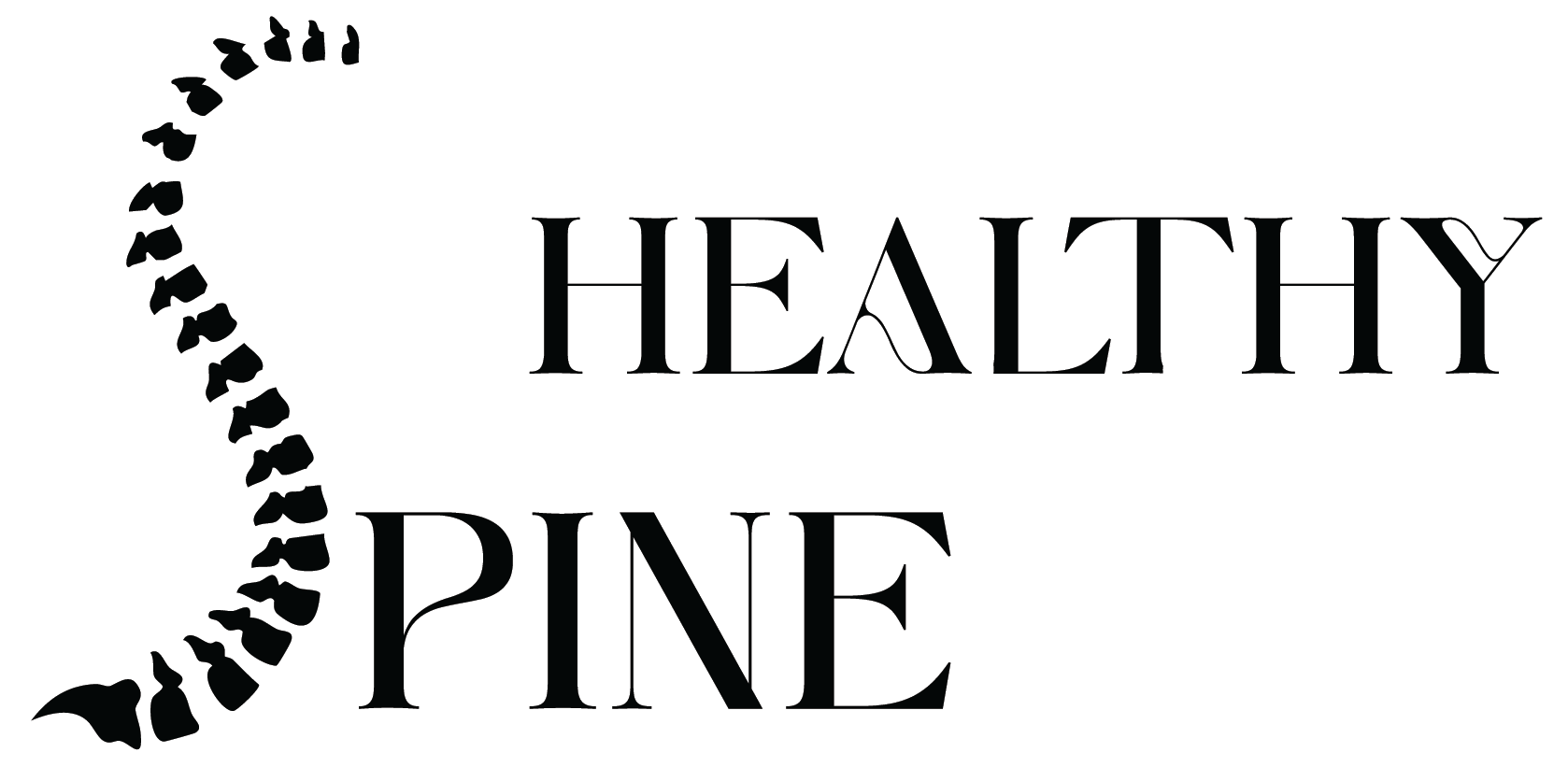The treatment of this type of deformity is particularly complex due to the severity of spinal and internal organ changes and requires a two-stage surgical approach.
Valeria, 13 years old.
She presented to the pediatric vertebrology clinic with complaints of severe spinal deformity and back pain, as well as weakness in the lower limbs, which made it impossible for her to walk the distance to school (about 1 km). Over the past year, she frequently experienced shortness of breath, recurrent pneumonia, and sleep disturbances due to pain.
Medical history:
At the age of 6, she was first hospitalized in an orthopedic department for conservative treatment, which continued in other medical institutions. From age 6 to 8, she wore a brace as recommended by a rehabilitation specialist. She stopped wearing it due to its ineffectiveness and significant discomfort.
Until the time of her visit to the clinic, the girl had never been examined by a pediatric vertebrologist!
Clinical examination upon admission:
- General condition – Severe.
- She moves slowly and with difficulty.
- Bending in all directions triggers pain and is severely limited.
- Muscle mass is poorly developed.
- Skin is pale.
The examination revealed:
- A severe chest wall deformity
- The right shoulder is significantly higher and longer
- Examination in the lying position was not possible due to severe pain
- A major spinal and thoracic deformity to the right in the frontal plane from Th2 to Th12
- A sharp rib hump with its apex at Th7–Th10
- Significant scapular asymmetry
Hospitalization:
Paraclinical examinations revealed significant multi-organ changes and anemia.
A spirometry and lung scintigraphy indicated severe pulmonary dysfunction – Grade IV.
The patient underwent a course of medical and orthopedic treatment aimed at improving the function of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems, in preparation for surgical intervention.
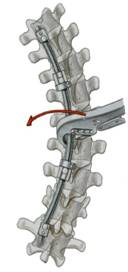
Stage I – Anterolateral Transthoracic Approach:
As in other particularly severe deformity cases, two transthoracic approaches were used—through the 6th and 11th ribs.
Stage II – Dorsal Deformity Correction:
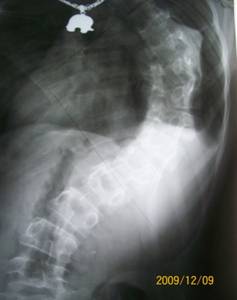
Fixation with a CD metal construct system
Total facetectomy (removal of the lower and upper facets) along the corrected segment (Ponte technique)
Thoracoplasty (removal of the rib hump)
 |  |
 | |
| Before surgery – 132° | After surgery – 28° Deformity correction – 104° |
She was mobilized (stood upright) 10 days after the surgery and discharged on day 21.She comes in for scheduled annual check-ups.
She has no complaints, the deformity correction is maintained, and she attends school.