Features:
– Even at Grade III deformity, significant degenerative changes are observed, such as:
pain syndrome with functional limitations, myeloischemia, and myelogenic intermittent claudication, which leads to early disability of the patient.
– Conservative treatment is generally ineffective, which underscores the importance of surgical intervention.
– Surgical treatment is challenging due to the severity of degenerative-dystrophic changes.
– There is no universally accepted surgical treatment algorithm.
Progression of dysplastic left-sided lumbar scoliosis.
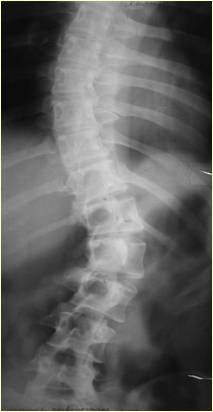 | 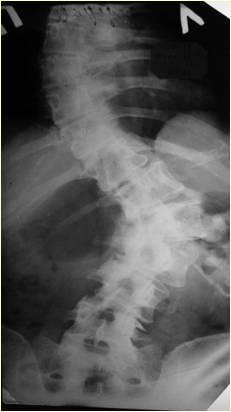 |
| 1962 – 16 years old | 1984 – 38 years old |
Surgical treatment of lumbar scoliosis aims to achieve the following goals:
- Relief of clinical and neurological symptoms of the disease
- Correction of spinal deformity and restoration of anatomical relationships in the lumbar region
- Prevention of further progression of the deformity
According to these goals, surgical treatment involves:
- Adequate decompression of the spinal canal and nerve structures
- Stable fixation and correction of the lumbar spine using modern metal constructs
- Creation of posterior and interbody spinal fusion (spondylodesis)
- Restoration of the height of the intervertebral space and foraminal openings
Indications for surgery:
- Persistent lumbar pain (lumbalgia), lumbar sciatic pain (lumboischialgia) that does not respond to conservative treatment
- Myelogenic intermittent claudication
Clinical case:
Patient, 13 years old. Lumbar scoliosis, Grade III. Degenerative-dystrophic changes in the lumbar spine. Myeloischemia, symptoms of intermittent claudication.
Before surgery: 35°
Combined spinal canal stenosis due to protrusion and thickening of the ligamentum flavum.
After surgery:
Operation included:
- Mobilization of the deformity using the Shulutko method
- Partial facetectomy
- Deformity correction and fixation with a transpedicular frame system
- Autospinal fusion (autospodylodesis)
After surgery:
100% correction of the deformity.
Pain syndrome and neurological symptoms regressed.